There are many Android devices available in the market and unfortunately, most Android devices still come with a default 16GB internal storage. Thankfully, most mid-range or low-end smartphones come with an SD card slot. However, there are many types of microSD cards available in the market, each having different parameters and capacities. Choosing a correct microSD card is essential, to get the maximum value out of the card. In this article, we tell you everything you need to know to pick the best microSD card for your Android device:
Specifications and Compatibility
There are three main types of microSD cards available in the market:
- SDSC or SD (Secure Digital Standard Capacity) — There capacities range from 128MB to 2GB. They utilize FAT16 file system and will work with devices that support SD, SDHC, or SDXC. For example, SanDisk 2GB microSD is the cheapest SD card available in the market.
- SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity) — There capacity on these cards range from 4GB to 32GB and utilize FAT32 file system. Because SDHC works differently than the SDSC cards, this new format is not backwards compatible with devices that accept only SD cards. For example, Lexar 32GB microSD is a decent class 10 SDHC card. When you buy a SDHC card, do make sure to look out for the SDHC logo.
- SDXC (Secure Digital Extended Capacity) — Their capacities range from 64GB to 2TB and utilize exFAT file system. Because exFAT file system works differently than the SDSC and SDHC cards, this new format is not backwards compatible with devices that accept only SD or SDHC cards. For example, SanDisk 200GB microSD is the class 10 SDXC card you can buy. Again, look out for the SDXC logo when you are buying an SDXC card.

Brands
You should always buy a microSD card from a reputable brand. It’s easy to buy a cheap, generic microSD card from eBay or black market but if you do so, you risk your data to get corrupted. According to this report from counterfeitreport.com, eBay accounts for maximum fake microSD cards. While you could get a fake microSD card from Amazon, check out the review, seller profile, and authenticity of reviews with fakespot.
Shopping from a reputable online electronics store is also a safe bet. With a branded microSD card, you can expect better performance, reliability, protection against shock, water, and even airport X-rays. You also get warranty and access to recovery software, in case the SD card fails. Some of the popular brands are SanDisk (SanDisk Ultra, SanDisk Extreme), Samsung ( Samsung EVO), and Transcend (Transcend Premium, Transcend Ultimate).
Capacity
The oldest SD specification format supports cards with capacities up to 2GB. SDHC format, announced in 2006, supports cards with capacities up to 32GB. On the other hand, SDXC format, announced in 2009, supports cards up to 2TB. At this point, the vast majority of Android devices support SDHC. SDXC is newer, but slowly gaining more popularity.
When it comes to Android device with microSD card support, you have to see the maximum capacity it can support. The manufacturer specifies them in the specs sheet and says something like this “expandable storage via microSD card up to 128GB.” This means that your Android device supports SDXC format with a maximum capacity of 128GB. So you can either buy a 128GB microSD card or anything less than that.
Since SDXC format is backwards compatible, you can also purchase an SDHC compatible microSD card with its capacity up to 32GB. For instance – Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge supports cards upto 256GB, Moto G4 Plus 128GB, and HTC 10 256GB.
Speed Class Rating
There are wide discrepancies in memory card transmission speeds among different SD memory card manufacturer and brand. Varying speeds makes it difficult to determine which card will provide reliable speed. The SD Association that creates standards for these products, don’t specify the exact speeds but instead provide guidelines and denote them in “speed classes.” The term speed class define two specific protocols:
-
SD speed class
They include speed class 2, 4, 6, 10 and denote the minimum write speeds in MB/s. A class 2 microSD card has a minimum write speed of 2MB/s, while a class 10 has a write speed of 10MB/s. Class 2, 4, 6 all have similar applications and work well, if you just want to take and store still photos, occasionally record high definition videos (720p max ), or want to store music and videos.
![]()
Class 2 cards are too slow, so you might want to avoid them at all cost even for the cheapest digital cameras. Class 4 and 6 cards may be a cost-effective option if you’ve basic needs. Although there is no harm on using class 10 cards, it’s more likely a value issue than technical.
Class 10 card allows you to take full HD video recording (1080p) at 60fps, HD still consecutive recording and RAW photos. Since all budget Android devices nowadays supports HD video recording, it makes sense to buy a Class 10 card. It performs better while taking photos, multiple burst shots of photos, and during file transfer.
An SD card’s speed class is easy to identify — you’ll see it on the online store listing or on the card’s packaging. For example, in this photo you can see a class 4 and a class 6 microSD card.
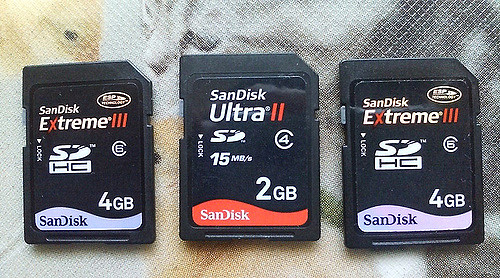
-
UHS Speed Class
Smartphone camera are evolving at a faster pace. You can record a 4K UHD video, take high resolution photos with optical image stabilization and high dynamic range, and record slow-mo video at greater than 60fps. In 2009, SD Association introduced UHS speed class designed for SDHC and SDXC cards. UHS utilizes a new data bus interface with higher theoretical read and write speeds.
- UHS I has a bus speed of — 35, 50, and 104MB/s
- UHS II has a bus speed of — 152 and 312 MB/s
UHS-I and UHS-II cards can use UHS Speed Class rating with two possible grades: class 1 for minimum read/write performance of at least 10 MB/s (‘U1’ symbol featuring number 1 inside ‘U’) and class 3 for minimum write performance of at least 30 MB/s (‘U3’ symbol featuring 3 inside ‘U’).
If you take and record lots of high resolution photos and 4K video, then microSD card with UHS-I speed class 3 is enough for this purpose. You don’t need a UHS speed class card for a budget smartphone. There are no smartphones which can take advantage of UHS II card, so you can safely avoid it. For example – SanDisk Extreme Pro is a 64GB, class 10, UHS-I class 3 card (you’ll see a symbol featuring 3 inside ‘U’). Samsung EVO is a 32GB UHS-I class 1 card (you’ll see a symbol featuring 1 inside ‘U’).

Android Version
Android has always had a limited support for microSD card. You can either use it to store photos, music, or videos or as a temporary storage for apps and games related data. However, Android 6.0 Marshmallow changed that with the introduction of the Adoptable storage feature, which lets you format a microSD card to act like internal storage.
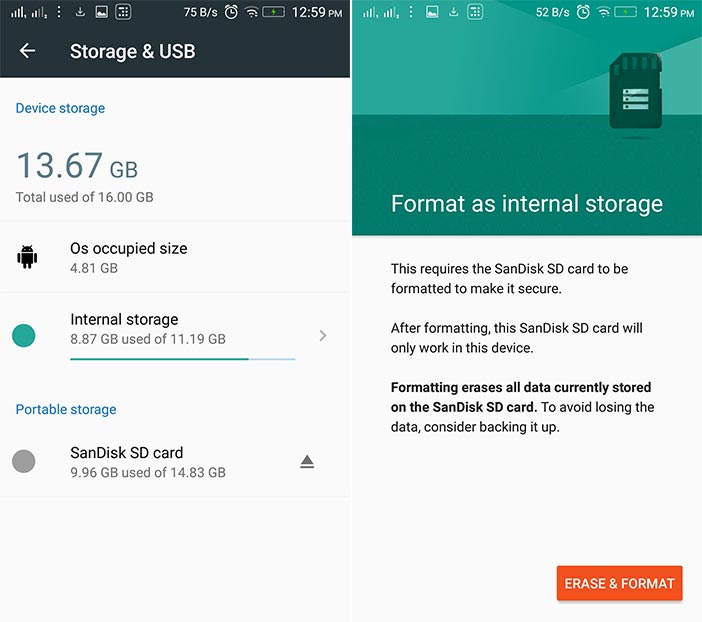
Once you adopt a new storage, it becomes a part of the system and is no longer removable. The platform runs a series of benchmark and compares its performance against internal storage. If your microSD is significantly slower, the platform will warn you about a possibly degraded experience with your phone. So, it’s important to choose a highest capacity and speed class microSD card. If your Android device supports 32GB, then go for 32GB SDHC class 10 card. For instance – Samsung Evo is a 32GB UHS -I class 1 SDHC card.
File System Support
FAT32 is the recommended file system for SD and SDHC cards. If you’re planning to use your microSD card with PC and Macs at any point, then you should leave as it is. FAT32 offers near-universal interoperability with every computing system, including PC and Macs. FAT32 doesn’t support files larger than 4 GB and volumes greater than 2TB, so that’s the only disadvantage.
But most microSD cards aren’t available in such high capacities, except for SDXC which supports exFAT file format. exFAT file system supports files larger than 4GB, and supports macOS 10.6.6 and above or Windows 7 and above. If you just plan on using the SD card on your Android device, you don’t have to worry about the file system.
SEE ALSO: 18 Essential Smartphone Accessories You Can Buy
Things to Consider While Buying a microSD Card
Concluding this article, there are plenty of things to consider when buying microSD card, and this guide will give you an idea which card to buy. If you stick with a reputable brand and understand your needs, then you should not face any problems with your purchase.
Do you use a microSD card or want to share something you know? Let’s know in the comments section below.

















Good article, but something is missing:
What is the exact reason that some Android devices support SDXC but only a certain capacity (128GB for example)? I assume I can’t operate a 1TB SDXC card in there… Why is that? What is it dependent on? The Android version? The firmware version? Both could be replaced by rooting the phone. Is it dependent on the hardware, e.g. the SOC? Please let me know. There is a big confusion also on many “phone comparison sites” that show different values (capacities) for the same device model…
Thanks!