Almost every portable electronic device today – be it our smartphones or electric vehicles come packed with the widely used lithium-ion batteries. They hold a limited charge, are quite bulky, need charging often and have a modest lifespan. That’s why, researchers have been hard at work to usher the most talked about alternative to lithium-ion batteries, i.e graphene battery.
Graphene batteries are said to be the absolute alternative to our current-gen lithium-ion batteries. Graphene batteries are itself quite lightweight, advanced and powerful. Graphene has been found to be a superior material as it not only has higher electrical and heat conductivity, but it’s also quite lightweight, flexible, and durable. Thus, graphene batteries have been under development for many years now and are expected to go mainstream in the next couple of years.
So, if you’re curious about graphene, graphene batteries and how they differ from your standard lithium-ion batteries, then you’ve landed at the right place. Here’s everything you’ll need to know about graphene batteries:
Note: This article involves the use of a lot of scientific and chemical terminology, but we have tried to simplify it as much as possible for your understanding.
What is Graphene? What are its Benefits?
Instead of diving straight into the world of graphene batteries, let me first tell you about graphene itself. I bet most of us learned in school that carbon exists in many different forms on the Earth, ranging from graphite to diamond. Well, that happens because of the varied arrangement of carbon atoms in different materials. The same is true for Graphene.
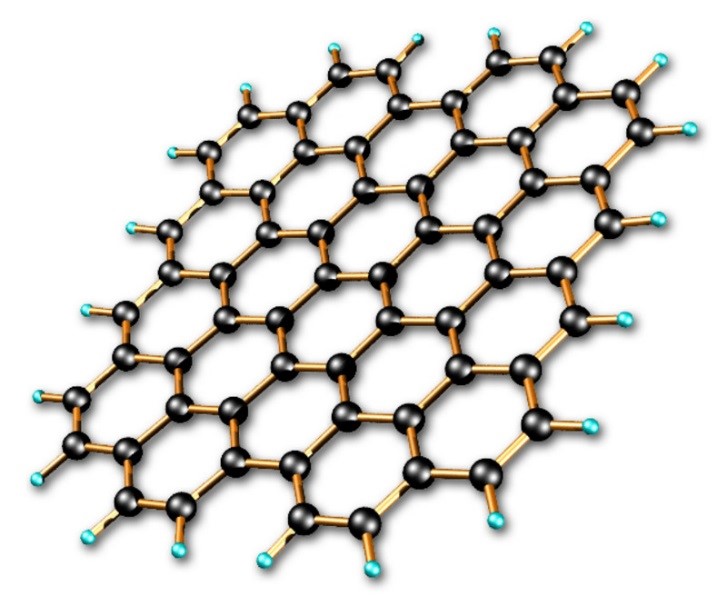
Graphene is a two-dimensional (2D) structure, where the atoms are laid out flat to form hexagonal carbon rings like a honeycomb. The structure is merely one atom high and is one of the most interesting discoveries of recent times, thanks to its properties. Though graphene is extremely thin, lightweight, and almost transparent, this material has come to be known as being stronger than Diamond and Steel. It’s super strong and is a great conductor of electricity too.
The flat hexagonal structure makes it simpler for electricity to flow with little resistance, offering improved electrical and heat conductivity better than the most conductive metal Copper. You don’t require any special conditions for the same as Graphene offers remarkable conductivity at room temperatures itself, thus, making it one of the perfect materials for the creation of next-generation batteries.
Graphene Batteries: How Do They Differ From Li-ion Batteries?
The internal structure of a graphene battery is quite similar to that of a standard lithium-ion battery pack. You have 2 electrodes and an electrolyte solution to enable flow of charge, but there’s a notable difference here. One of the electrodes in graphene-based batteries, mostly the cathode, is replaced with a hybrid composite material (solid-state metal + graphene) used in place of a standard solid-state metal.
While graphene batteries would prove to be way better than lithium-ion batteries really soon, researchers are now trying to improve battery performance for existing batteries using graphene. They could capitalize on this material’s conductivity and larger surface area in the anode to optimize lithium-ion batteries.
Researchers are also known to be working on hybrid materials such as Vanadium Oxide (VO2) and graphene, which could also be useful towards improved battery optimization, quick charge and discharge of the battery.
Benefits of Using a Graphene Battery
Graphene battery is a new technology, but it doesn’t mean they haven’t been tested. Manufacturers have dedicated quite some time to graphene battery research and why wouldn’t they, especially when it’s superior to the lithium-ion batteries we use right now. So, let’s take a quick look at the benefits of using a graphene battery:
- Smaller, slimmer battery: We have already discussed how graphene is lightweight. It’s when you stack 3 million layers of graphene is that you get 1 mm thickness. I mean, that should be enough to tell you that graphene batteries aren’t going to take much space in your future smartphone. It will allow manufactures to place higher capacity batteries in your phones, tablets, laptops, and more.
- Higher capacity: Graphene has a higher energy density as compared to lithium-ion batteries. Where the latter is known to store up to 180 Wh per kilogram, graphene’s capable of storing up to 1,000 Wh per kilogram. So, you can have a higher capacity graphene battery pack of the same size as the lithium-ion battery.
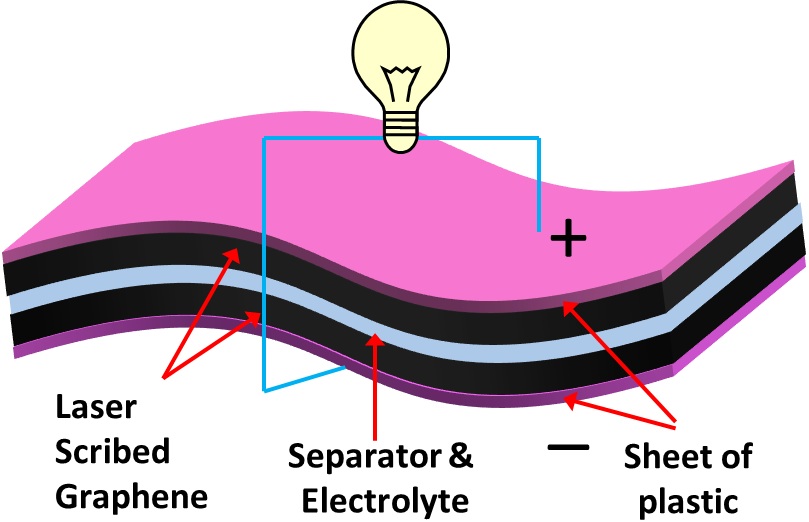
- Faster charging times: Graphene is a potent conductor of electrical energy as the honeycomb structure doesn’t offer any resistance to the flow of electrons. So, it can charge quickly, while also providing you longer battery endurance as compared to lithium-ion batteries.
- Thermal management: Yeah, you may have not guessed it but graphene facilitates better heat dissipation as well. It can reduce the battery’s operating temperature by up to 5 degrees, so your phone won’t heat up while charging or playing games.
- Greater Safety: Graphene batteries are expected to be a lot safer than lithium-ion batteries since the material is more flexible and stronger. This means future battery packs won’t need a ton of protective cases, taking less space and being lightweight.
To sum everything up, a graphene battery is going to make for a better choice over a lithium-ion battery in the coming years. It will be remarkably cheaper, smaller, lighter while offering greater electrical storage and faster-charging speeds.
Shortcomings of Graphene Battery
Graphene batteries have a number of benefits but the one shortcoming that’s holding its mass-adoption in our devices is mass production and the costs involved in the same.
Why is it difficult to mass-produce graphene batteries? Well, it’s because of the lack of a feasible technique for the mass-production of high-quality graphene. You certainly could produce graphene at home using graphite and sticky tape, but that doesn’t work for the mass production of the batteries. The lack of the same also drives up production cost as quality of materials will need to be taken into account, which could be as high as tens to thousands of dollars.
Currently, the graphene batteries are being developed in small numbers by a handful of manufacturers. But, others like Samsung are looking for ways to bring down the cost to make the next-gen batteries viable for use. The Korean giant is said to have figured out affordable means to produce graphene batteries and we can expect an update real soon.
Commercialization of Graphene Batteries
Graphene batteries have extraordinary potential and yield results better than the existing battery packs — something that should have become quite clear to you by now. Research in this field has been quite rampant in the past couple of decades, but we will still need to be patient for its commercialization.
Many companies are currently testing graphene batteries or are trying to improve lithium batteries with graphene to enhance their performance, but they’re not fully commercially available at the moment.
-
Samsung’s Graphene Research
Samsung SDI, the battery manufacturing arm of the Korean giant, is actively working in this field and has seen multiple breakthroughs over the past few years. First, we learned that Samsung had developed ‘graphene balls‘ that could make lithium-ion batteries last longer (while offering 45% increased capacity) and charge 5 times faster.

Samsung has since been silent about its graphene battery plans, except for a handful of appearances across car and electronics expos. However, there’s been rumors that a new graphene battery-backed smartphone is in the works at Samsung and it could be unveiled in 2020 or 2021. These batteries are said to fully charge in half an hour, remain operational at higher 60-degrees temperatures, but we are not aware of its capacity and composition at the moment.
-
Additional Research & OEMs
Apart from Samsung, there are a number of battery makers, like CellsX who’re already manufacturing and shipping graphene batteries to its partners. They have designed not only smaller battery packs for power banks (more on this below), but also made bigger batteries for model quadcopters and EVs as well. Huawei has also unveiled a graphene-enhanced Lithium-ion back in 2016 to offer longer operational time and facilitate heat dissipation.
While graphene batteries are yet to make an appearance on our phones, you could still charge them with a graphene battery-laden power bank. Yes, we have a few graphene battery power banks available in the market. Called the Apollo and Ultron, these power banks went for crowdfunding, got the number of backers they needed, and are already shipping these products. You can read all about these power banks right here.

On the other hand, renowned electric car maker Tesla and India’s Log9 are showing an interest in metal-air batteries. They involve the use of a graphene rod as the cathode since it’s porous and lets air pass through. Metal-air batteries can help increase battery efficiency by up to 5 times at one-third the cost, which sounds great.
SEE ALSO: Best Graphene Power Banks You Can Buy
Graphene Batteries Could be Game Changer
Graphene batteries are definitely the next big thing because carbon is in abundance as compared to Lithium, which is a rare metal. Manufacturers have been trying to use the graphene material in about everything since its discovery in 2004. So, we can expect a number of graphene-laden products, especially graphene batteries, to come to fruition within the next couple-odd years. They will still be restricted to select smartphones but we’ll at least have a working prototype on our hands soon. What are your expectations from graphene batteries? Are you excited for even larger batteries? Let us know in the comments below.


















I was recently reading up on graphene batteries and came across Graphene Manufacturing Group which makes aluminum-ion batteries. The aluminum-ion battery composition consists of an aluminum foil anode, a graphene cathode, and an aluminum-chloride electrolyte. No lithium or rare earth metals. Plus to make the graphene they use the carbon from methane leaving Hydrogen. Hydrogen is a clean burning fuel but never found where it says what they do with it.
I’d love to have some information about future battery packs ( 200-300 ah ) for caravans eg: size cost etc compared to lithium. These batteries sound awesome. I was thinking of purchasing Litium batteries for my van but I think I will hold of for now.
Graphene-enhance lithium-ion batteries are already in wide market use in China. In the city where I live, they power all of the ebikes for a major delivery service, and the company is working closely with a supercar manufacturer. They also produce a battery suitable for golf carts, drones, and tools. Bosch is using some of them for tools.
I hope the Graphene batteries are allowed to come to market and that they are also mined by different countries’ mining companies so we end up with a steady supply of the raw material and also that they find clean, efficient ways to process the Graphite into Graphene so we have a sustainable way to make safer, lighter, higher energy density batteries. It will revolutionize the transportation industry and home solar power industry as well as many other products that will serve humanity well.
Fred Stebbing: According to other sources Graphene was discovered around 2004. However, I think you may be referring to Graphite – which was discovered more than two centuries before. Graphite may have been in use for eons.
One more thought on Graphene. In my State of MI the State / Federal govt has put restrictions on WHICH COMPANIES may sell Solar+Battery systems for home use. They allow companies like Generac, but not Tesla, where the systems they allow are good, but about $40k more than Teslas for a lower power system. Michigan power companies like DTE, Consumres etc. have final say as to whether “they” will approve your purchase and how much power you may purchase for yourself – that is unless you totally disconnect their service. I think this is an anti-trust against the consumer. Any lawyers out there care to comment?
Full Graphene batteries are inert! Thus, are idea for automabiles and aeroplanes. Electric Aeroplanes will need this technology as current planes dump their fuel load when there is an issue, due to safety issues. Safer, fast charging, higher capacity and cost saving, will be key factors for adoption, once the manufacturers solve the mass production issues.
Graphene was first discovered in the previous century
Is it just me or did i discover a misnomer (closest description for an error I could come up with, while trying to be respectful)
If a battery capacity is 1000wh per kg vs 180wh per kg and the volume was the same then that would be impressive, but when you have a lighter material to make up 1kg in weight then you’d have have larger volume?
So unless I’m missing something then your cell phone, EV, or anything else for that matter is going to take up more space using a battery made up from graphene……..
its not only a question of density but also of the actual makeup of the material, the structure and capacity differs between lithium ion and graphene, that is what makes graphene a far better capacitor, it weighs less while at the same time handling more without having a higher volume over lithium ion.
Fred Stebbing – You have your cart before the horse on the Weight Size comment. If a Graphene battery is 1000Wh/kg and Li-Ion only 180Wh/kg then the Graphene battery can store 5.5 times the Energy per the space it takes. So it could be the same size as the Li-Ion and storing 5.5 times the energy. Or you could take the same space and be 2.5 times lighter. So a car that normally weight 4,200lbs would weight less than 3,500lbs and travel 1,650 miles on a charge. It would take only about 30 minutes to obtain 92% charge with a level 3 charger for that 1,600 mile trip! And the cost would be less for the vehicle as well so it is a win win for the consumer. Of Course, the socio-economic outcome will be based on the greed of corporations who are already setup to manufacture Li-Ion but the cost of those batteries will go down as well due to pricing parity which will be forced by Graphene batteries. Check out which countries have the Largest Graphite Deposits (China, Brazil, India, Canada…)
I’m principal investigator inventor of a breakthrough in propulsion physics and technology, large graphene batteries for trucks and aircraft might power my breakthrough propulsion system?
Sounds great…. if high end batteries with loaded power in smaller sizes could be produced, could be a game changer to green house Gas..
Vehicles and Avaition could reduce massive carbon from our beautiful environment……
Very Interesting. Does a Graphene Battery have the same safety concerns with catching on fire like Li-Ion?
I would assume not if assembled correctly, it has fantastic heat dissipation qualities.