Leaving the popularity of NFTs and the metaverse in the dust, AI has emerged as the new buzzword in the technology world. ChatGPT and its alternatives are flourishing on the internet, helping users get everyday tasks done with ease. Earlier, we published guides on how to get started with making your own ChatGPT-like chatbot, using Bing AI in any browser, and more. But, what if you are a Linux user and want to bring the wits of this AI chatbot to your system? Well, this is where ShellGPT steps into the picture. It brings the power of ChatGPT right to your Linux Terminal. ShellGPT provides answers, intelligent suggestions, and writes commands and code for you, helping you navigate the command line efficiently. In this article, we will show you how to install the ShellGPT command line tool and use a ChatGPT-like AI bot in the Linux command line.
What Is ShellGPT for Linux?
Developed by Farkhod Sadykov (along with two other contributors, namely Eric and Loïc Coyle), ShellGPT is a command line version of ChatGPT that enables users to engage with the AI chatbot in their Linux terminal. It is based on OpenAI’s GPT large language model (read more about OpenAI’s new GPT-4 model right here).
ShellGPT can provide intelligent suggestions and recommendations and can even execute shell commands based on your text input. It also learns from your interactions and becomes more accurate over time. With this ChatGPT tool baked into the command line, users don’t have to type long commands or remember complicated Linux Terminal commands. They can save valuable time while minimizing errors, getting ChatGPT to do some of their menial work for them.
Prerequisites to Install ChatGPT in Linux CLI
Here are some of the prerequisites you need to fulfill before you can install ShellGPT on your Linux system. These are not too complicated tools and can be installed with some simple commands.
Install Python
Python is an indispensable tool, and like many other Linux tools and libraries, ShellGPT (command line version of ChatGPT) is also built on Python. In fact, ChatGPT is also built using Python along with other languages. Generally, Python comes preinstalled on most latest Linux distros. So first, check the python version installed on your Linux PC with this command:
python3 --version
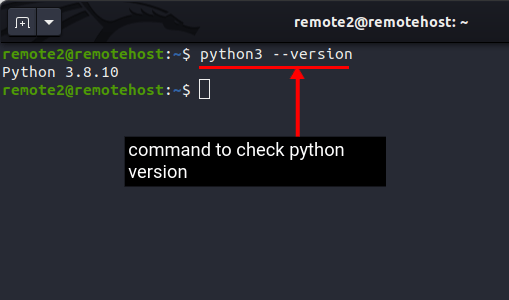
If the above command outputs any errors, it means python is not installed or the deprecated python2.7 is installed on your system. Then, you can use our guide on how to install python in Linux.
Install Pip Package Manager
Pip is a cross-platform package manager for Python. It helps manage various Python packages and libraries required to bring ChatGPT to Linux. You can install, upgrade, and uninstall the required packages using a single command. It generally comes preinstalled with Python in most Linux distributions, but if it is not installed, you can install it with this command:
sudo apt-get -y install python3-pip

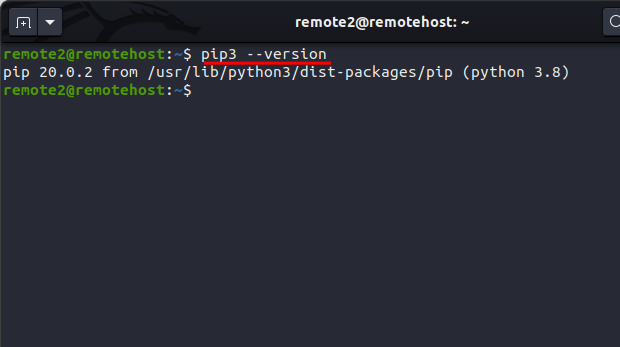
Once installed you can check the Pip version installed in Linux with the following command:
pip3 --version
Install Venv Module
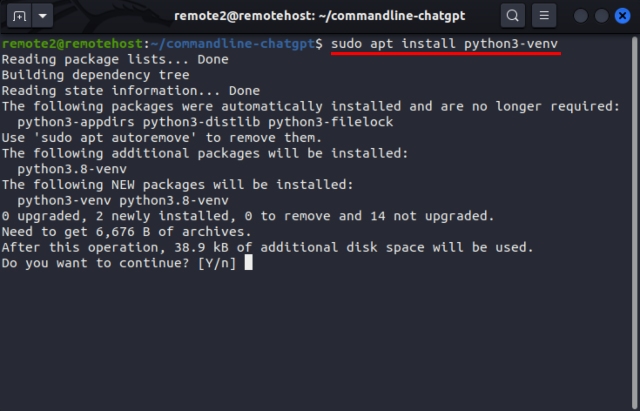
This module is not necessary for ShellGPT or ChatGPT, but we recommend you install it to create an isolated virtual environment in Linux to prevent any conflict with other libraries. Installing any library or package will install many background dependencies that can interfere with other libraries. To create a virtual environment for a project, you need the “venv” module, which can be installed using the command below:
sudo apt install python3-venv
Set Up ShellGPT to Use ChatGPT in Linux Terminal
We have divided the instructions to install ShellGPT on your Linux PC into four different sections to make it easier for you to understand. Let’s start with setting up the environment, followed by getting the OpenAI API key, and installing the chatbot in the Terminal.
Set up the Environment
Now that you have the dependencies covered, let’s create the environment to access ChatGPT from your Linux terminal with the following steps:
1. First, open the terminal from the app menu or use the “Ctrl + Alt + T” keyboard shortcut.
2. Now, use the command below to create a new directory and keep all the files organized.
mkdir <your_directory_name>
For example, we have created a new directory with the name “commandline-chatgpt” with the command below:
mkdir commandline-chatgpt

3. Then, switch over to the new directory you just created with the “change directory” command:
cd <new_directory_name>
In the example below, we have move to the commandline-chatgpt directory, where we will create the environment to use ChatGPT in the Linux terminal:
cd commandline-chatgpt

4. Now, use the command below to create a virtual environment with the venv module. We have used the “chatgpt_cli” name for our virtual environment.
python3 -m venv <virtual_environment_name>
For example: python3 -m venv chatgpt_cli

5. The virtual environment you just created will be deactivated by default. To activate the environment, use this command:
source <virtual_environment_name>/bin/activate
Once you execute the above command, the shell prompt will now display the name of the virtual environment in brackets, like this:
(<virtual_environment_name>)<username>@<system_name>
As you can see in the image below, the default Linux shell prompt changed to (chatgpt_cli) remote2@remotehost upon running the commands above.

Get Your OpenAI API Key
In order to use ChatGPT’s services in Linux, you will need an OpenAI API key. Currently, OpenAI is offering $5 credits for trial use. Once you exhaust the credits, you need to pay for access to the API. That said, here’s how you can get an OpenAI API key for this command line ChatGPT chatbot:
1. Navigate to OpenAI’s website (visit) and create a new OpenAI account. If you already have an account, simply log in and move to the next step.
2. Next, click on your profile image at the top right corner and select “View API keys” from the drop-down menu.

3. Here, you will see all the previously generated API Keys if any. To generate a new API key, click the “Create new secret key” button.
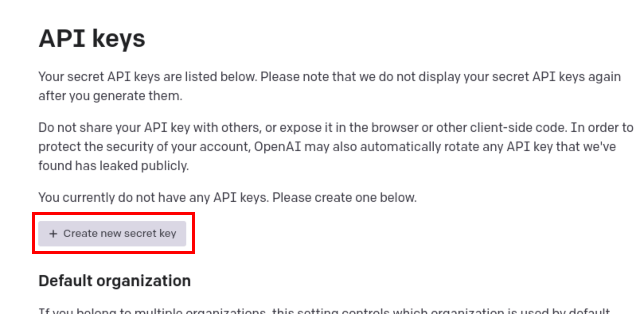
4. A new pop-up box will open with your API key. Do not share this API key with anyone or share it publicly. Copy your API key in a secure file or location, as you can only view it once. You won’t be able to copy the API key after you click “OK” here.

5. Now, create an environment variable for this API key with the command below. In Linux, you can create an environment variable using the “export” command. Replace <your_OpenAI_API_key_here> placeholder with the actual API key you generated to use ChatGPT in the Linux terminal.
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your_OpenAI_API_key_here>

6. Verify the environment variable by listing it with the env command:
env

7. This variable is only temporarily stored for the current session. To store the API key permanently, open the .bashrc file in the text editor of your choice and add the variable at the end of the file.
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your_OpenAI_API_key_here>

8. Save the file and exit the text editor after you have added the OpenAI API key. Now, run this command for the changes to take effect:
source .bashrc
9. Finally, verify the changes with the env command:
env

Install ShellGPT to Use ChatGPT
Having finished setting up the environment, you can now proceed to install the command line version of ChatGPT in Linux. You need to omit the –user flag if you are installing it in a virtual environment. Now, use the command below to install ShellGPT on your PC:
pip3 install shell-gpt --user

ShellGPT: Syntax & Options
Now that you have installed ShellGPT, you must be eager to use it for various tasks. But before that, let’s check out the syntax and some options that we can use to make our outputs interesting. Using ShellGPT for multiple tasks is easy, thanks to its straightforward syntax:
sgpt <options> <input_query>
Some of the options you can use with the ShellGPT (sgpt) chatbot are:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
--temperature | Changes the randomness of the output |
--top-probablity | Limits to only the highest probable tokens or words |
--chat | Used to have a conversation with a unique name |
--shell | Used to get shell commands as output |
--execute | Executes the commands received as output from --shell option |
--code | Used to get code as output |
How to Use ChatGPT in Linux Terminal (Examples)
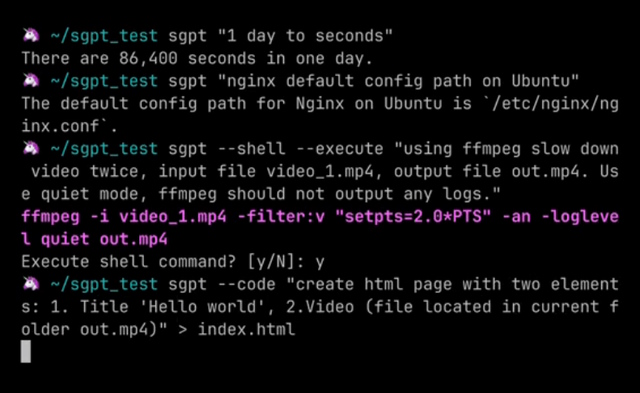
1. Use ShellGPT for Queries
You can use ShellGPT as a search engine for any sort of query. Since it is an AI chatbot, you get results with more human-like answers and not a series of ranked web pages like most search engines. The syntax to use ShellGPT to get answers to your questions is:
sgpt "<your_query>"
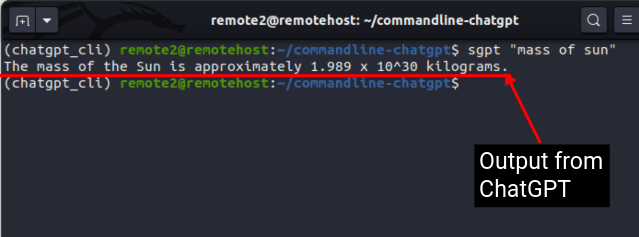
For example, if you need to know the mass of the sun, use this command:
sgpt "mass of sun"
You see a nice animation in the Terminal while ShellGPT tries to get a response. The response we received is highlighted underneath. You might get a similar reply depending on how the model is trained:
The mass of the Sun is approximately 1.989 x 10^30 kilograms.
2. ChatGPT Chatbot Mode
If you had used ChatGPT for chatting, you must have felt that it is responses are no less than a human. Now with the help of ShellGPT, you can even use ChatGPT right from your Linux terminal. Simply use the --chat option followed by a unique session name and a prompt.
sgpt --chat <unique_chat_session_name> <input_prompt>
For instance, if you want to ask ChatGPT to tell you a joke, use this command:
sgpt --chat joke "can you tell me a joke?"
Once you run the above command, you will get the following result as output:
Sure, here's one:
Why couldn't the bicycle stand up by itself?
Because it was two-tired!
3. Generate Code
You can even use the CLI-based ChatGPT tool to solve coding problems or generate code snippets. Simply use the --code flag to generate code for your prompt, as shown here:
sgpt --code "<input_prompt>"
For example, if you want to solve the classic Fizz Buzz problem using python, use this prompt:
sgpt --code "Solve classic fizz buzz problem using Python"
ChatGPT will quickly give you an output, which you can then paste into your code editor and test it out:
for i in range(1, 101):
if i % 3 == 0 and i % 5 == 0:
print("FizzBuzz")
elif i % 3 == 0:
print("Fizz")
elif i % 5 == 0:
print("Buzz")
else:
print(i)
4. Generate Shell Commands
While the Terminal can be a powerful tool to execute complex commands and automate tasks, it can sometimes be difficult for novice users to remember the syntax and options of various Linux commands. With ChatGPT in your command line, you can not only get the syntax of a Linux command but also get the exact command with the parameters and options required. Simply use the --shell flag as:
sgpt --shell "<input_prompt>"
For example, if you need to set the read-only permission for all files in the current directory, use the command:
sgpt --shell "Make all files in the current directory read-only"

As expected, ChatGPT delivers and returns this as the output:
chmod -R a-w .
Furthermore, if you use the --execute and the --shell flag together, you can even execute the shell command generated directly. As for the above example, here’s what the syntax looks like:
sgpt --shell --execute "make all files in current directory read-only"

You will get the following output:
chmod -R a-w .
Execute shell command? [y/N]: ySo yeah, ShellGPT brings the power of ChatGPT right into your Linux terminal. It not only makes working with the command line simple for both beginners and seasoned users but also brings you additional features. And as we mentioned above, it becomes more useful over time as it is designed to learn from users. But remember not to share any sensitive information or data, especially proprietary code from your company, with any kind of AI model. That said, do let us know what you think of this AI command line tool in the comments below.