- DNS or Domain Name Service converts human-understandable web addresses into machine-understandable IP addresses.
- If your device's DNS server isn't working, you may want to flush the DNS cache or restart the device.
- Among other fixes, you can try disabling an app on your firewall, restarting your router, or raising a support ticket to your service provider.
DNS or Domain Name Service is an important system that translates human-readable web addresses to machine-readable addresses called IP addresses. That’s right, the internet doesn’t directly understand your “Google.com” search but relies on DNS to first convert it into an IP address. However, the DNS server may not respond sometimes due to unknown reasons, so here are eight fixes you can try if your DNS server isn’t responding.
Method 1: Restart your Device
One of the easiest solutions you can try if your device’s DNS server isn’t responding is by restarting your device. While this isn’t a sure-shot way of solving the issue, the amount of high-severity issues a simple restart is capable of solving cannot be neglected.
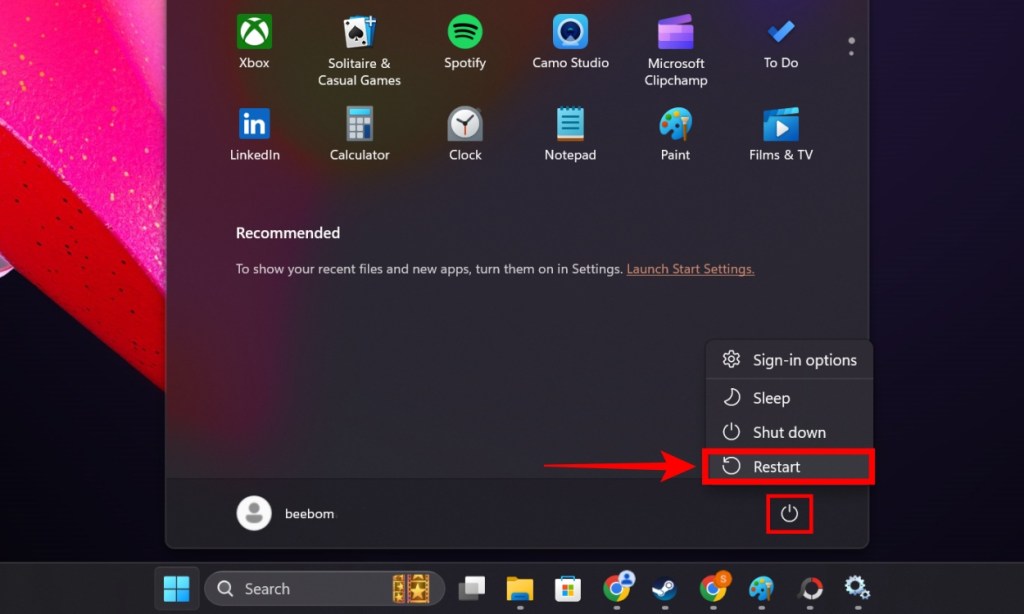
- On Windows, go to Start > Power Icon> Restart.
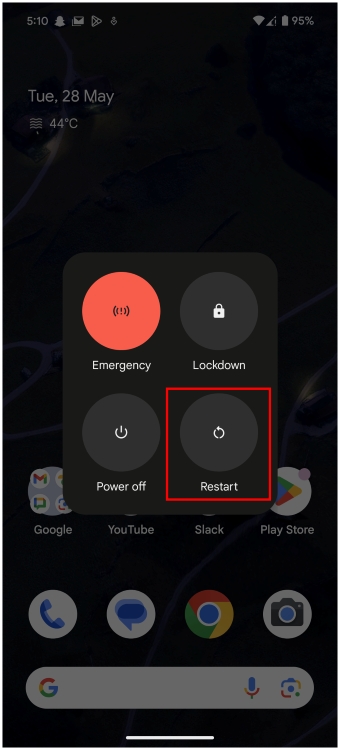
- On Android, long-press the Power button or press the Power + Volume Up button and tap on Restart.
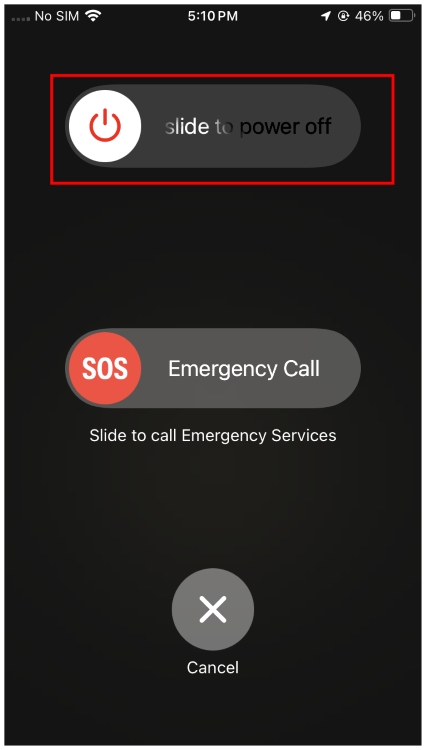
- On iPhone, press and hold the Side button + Volume Up button and drag the slider to the right to turn off the device. Wait for 30 seconds and long-press the Side button until the Apple logo appears to turn it on. Check out dedicated Restart iPhone guide to learn how to reboot another iPhone.
Method 2: Try a Different Browser, DNS, or Device
Trying a different browser will help you determine if there’s an issue with the browser. Similarly, trying a different device will help find out if the device’s DNS server settings were changed and are the reason why your device’s DNS server fails to respond.
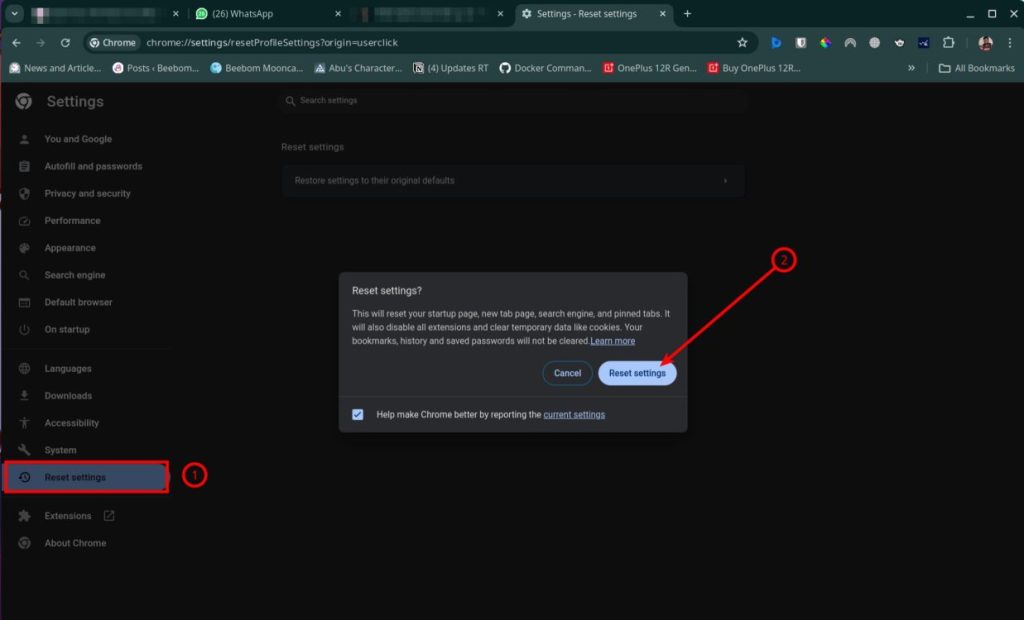
You could try resetting your Browser’s network settings by going to Settings > Reset Settings.
If the browser’s default DNS isn’t responding, you could try switching to a different DNS like Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1, NextDNS, or OpenDNS. The option to switch the default DNS in Chrome is located in the advanced section under Privacy and Security.
Method 3: Flush DNS Cache
You can easily flush the DNS cache from the Windows terminal. Here’s how to do it.
On Windows
- Launch Command Prompt.
- Type the following command and hit the Enter key to flush the DNS cache.
ipconfig /flushdns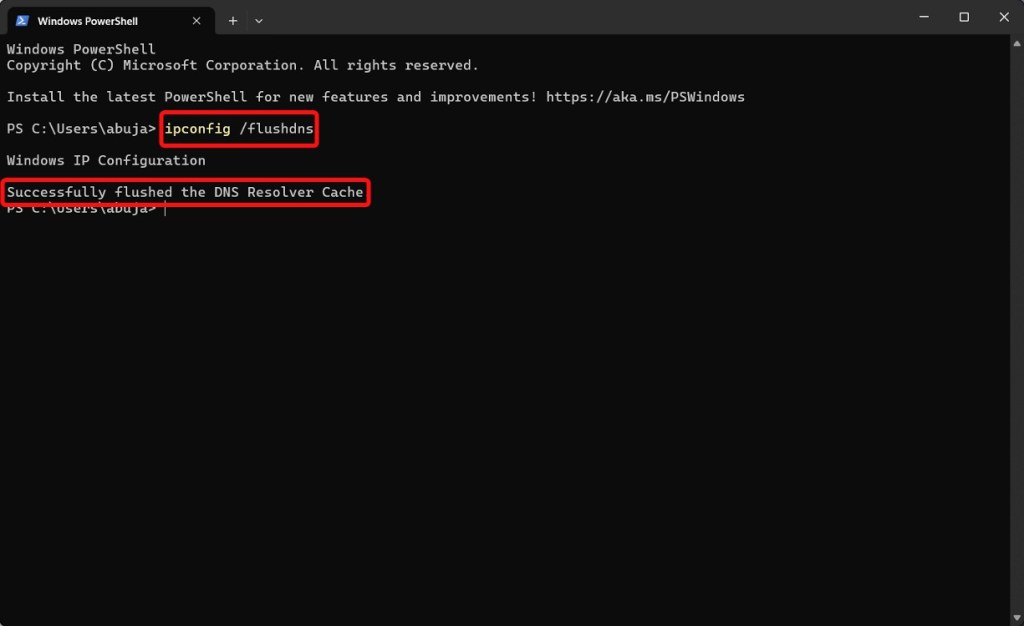
This will remove the remnant DNS cache from Windows and should hopefully help you freely browse the internet again.
On Mac
- Launch the Terminal app from the Launchpad or search for it on Spotlight using the Command + Space keyboard shortcut.
- Type the following command and hit the Enter key.
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder- Enter your Mac password and then press the Enter key again.
This will reset your DNS cache immediately.
Method 4: Restart Your Router

Your router holds the key to the gate that allows you to browse the internet without hiccups. Hence, if the DNS is unresponsive, it is possible that there might be something wrong with the traffic router or there might be congestion if lots of devices are connected to the same network. In that case, you might want to turn off your Wi-Fi router and give it a gap of at least a few minutes before turning it on.
Method 5: Reset DNS Settings
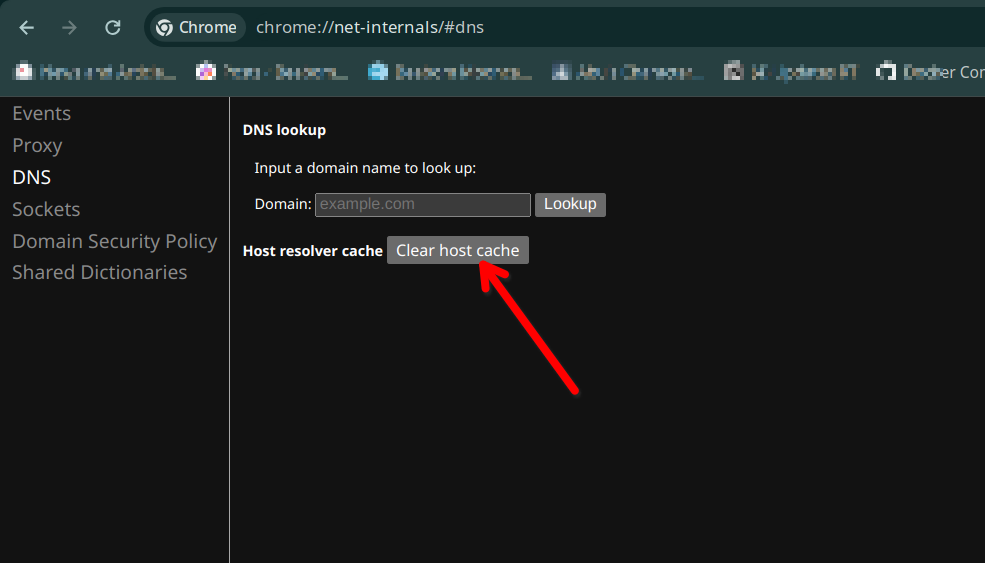
If your device’s DNS is not responding, you can try resetting the Host cache from the browser by going to chrome://net-internals/#dns from the address bar and clicking on the Clear host cache button. This works on all major platforms, including Linux. Once done, try searching for a domain name, and it should start functioning as usual.
Method 6: Allow an App Through Firewall
There are times when an Antivirus or Firewall can break DNS. This doesn’t happen often and commonly but it could as well be one of the reasons why your DNS server shows that it’s unresponsive. If you’re using third-party Antivirus software, we’d suggest disabling the protection. Try browsing and check if the DNS is functional again.
If you don’t have a third-party Antivirus but Windows Security, try disabling the firewall for your web browser app.
On Windows
- Go to Windows Security > Firewall & network protection > Allow an app through firewall.
- You can then remove Google Chrome from the firewall by navigating to Change settings > Google Chrome > Remove > OK.
On Mac
You can also allow an app through macOS’ Firewall using the steps below.
- On your Mac, go to System Settings > Network > Firewall > Options. On older macOS versions, you may need to navigate to System Preferences > Security & Privacy > Firewall > Firewall Options.
- Now, click on the plus + icon, locate and select the web browser app from the Applications folder and click on Add.
- The app will now appear inside the list of apps and services. To make sure the app has complete access to network connections, click on it and select Allow incoming connections from the dropdown menu.
- You can now click on OK to save changes.
Method 7: Update Your Computer
Microsoft pushes the latest security updates quite frequently, and it is possible that your computer might not be running the latest version of the security. This could be a reason why DNS is not responding on your Windows or Mac computer.
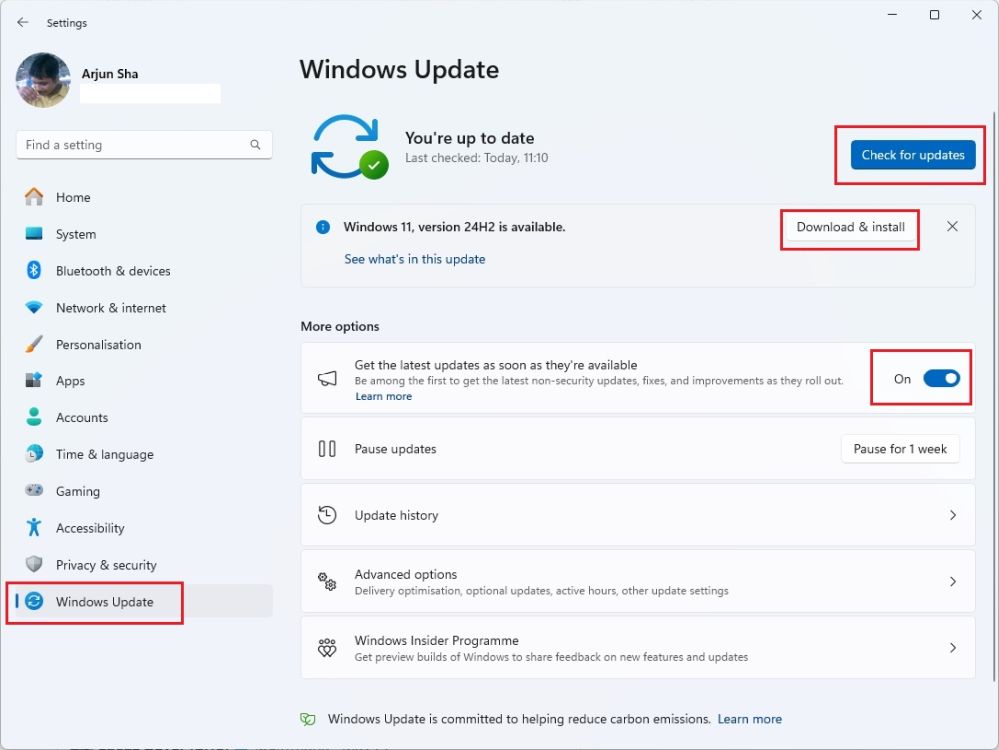
- To update your Windows PC, go to Settings > Windows Update > Check for updates.
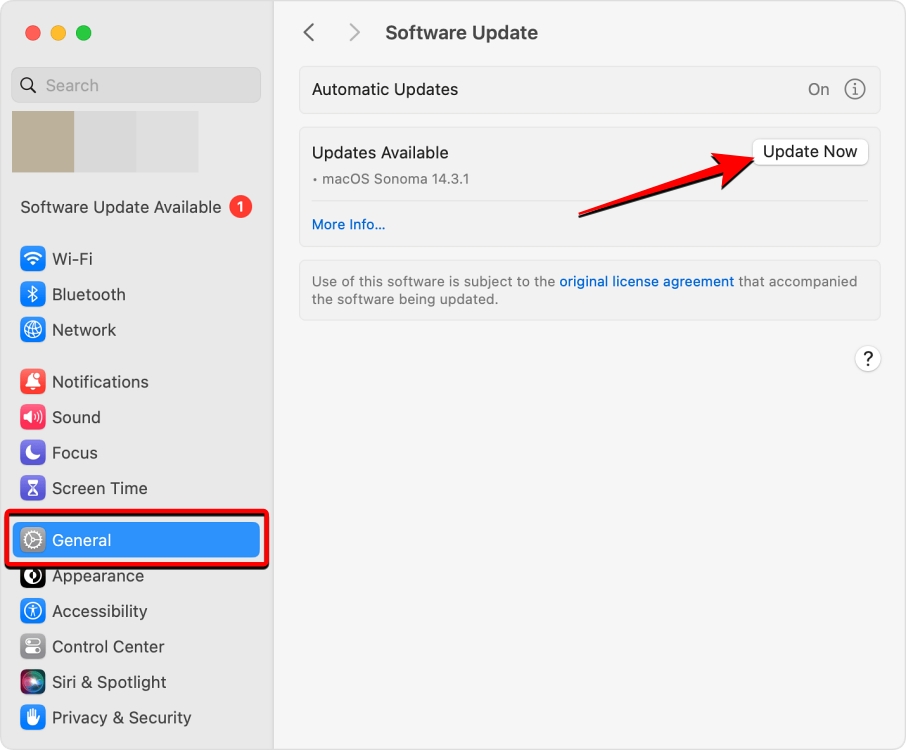
- To update your Mac, go to System Settings > General > Software Update > Update Now.
Method 8: Check with Your Service Provider
Oftentimes, some of the common issues you face with your internet are due to the service provider. Perhaps a few of its services in some areas might be down, and your area might be impacted. A quick call or help ticket to your service provider should help you determine if the service provider is at fault and ask them to solve your DNS issues at the earliest.
These are some solutions you can try if your DNS server is not responding. If none of the solutions have worked for you, you may try resetting Windows without losing your personal data. Doing so should reset your Windows installation and its settings to factory state, and your DNS woes may be solved thereafter.
Have you ever faced issues with the DNS server? Let us know in the comments below.