- Deep learning uses multi-layered neural networks that learn from data through predictions, error correction and parameter adjustments.
- It started with the introduction of neural networks in 1950, breakthroughs like backpropagation in 1986, powerful GPU computing in 2000s, and introduction of the Transformer architecture in 2017.
- There are various deep learning models such as CNNs which are used for image recognition, GANs for synthetic data generation, transformers for language models, and more.
Whenever the topic of AI comes up, people talk about deep learning in AI and training their models, and other such technical jargon. But what exactly is deep learning, and what does it have to do with AI? Well, that is what I will help you understand, exploring deep learning in AI, how it works, and its different applications in the field.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning in Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to a set of methods to train multi-layered neural networks to learn from large amounts of data. It works like your brain, which learns patterns, behaviors, distinct features, or qualities to recognize things around it.
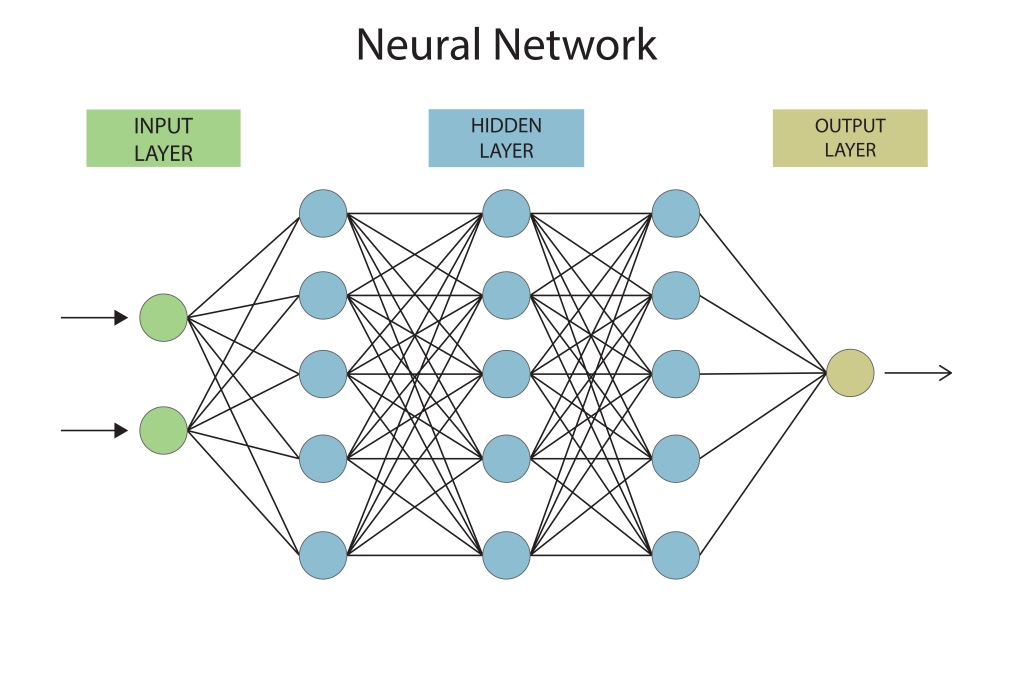
It uses neural networks made up of multiple layers of interconnected nodes, hence the name “deep”. These nodes help process raw data through calculations and continuous corrections. This is used in modern AI systems for things like image recognition, language translations, chatbots, and even Agentic AI models, which also heavily rely on deep learning.
How Deep Learning Works?
Let me give you a simple breakdown of how deep learning sees information, learns from it, and offers a prediction related to it.
- Input Layer: Takes in the raw data. For example, a photo of an animal.
- Forward pass: Input data passes through the neural network to produce predictions.
- Compute loss: A loss function measures how wrong the prediction was.
- Backpropagation: The loss value is sent back, and the network makes adjustments to reduce the chance of another wrong prediction.
- Optimizer step: The Optimizer uses the wrong prediction to adjust the parameters so the mistake does not happen again.
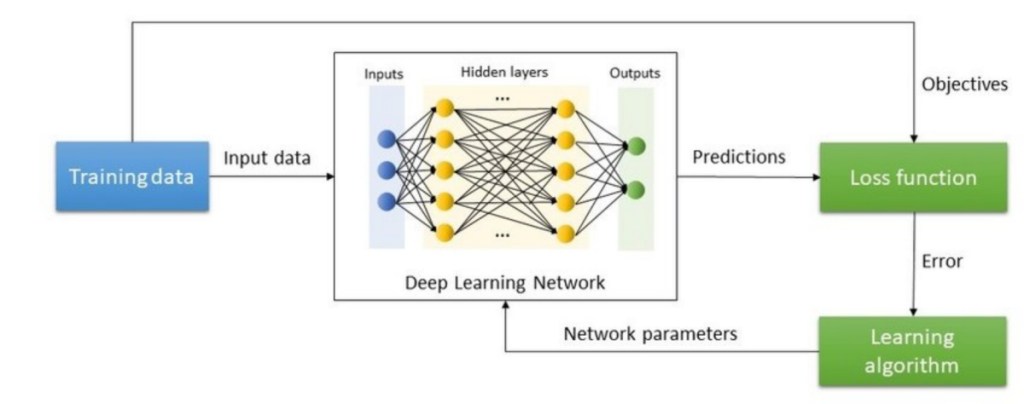
This cycle repeats thousands of millions of times until the deep learning AI makes accurate predictions consistently.
The Evolution of Deep Learning in AI
Deep learning might sound like a new concept since you might have only recently started hearing about it. But its roots go back decades, starting with early pioneers who developed AI. Let me give you a quick recap of the evolution of deep learning.
- AI Becomes a Field of Research (1956): John McCarthy organizes the Dartmouth Conference, coining the term ‘artificial intelligence’ and develops LISP, one of the first languages for AI research.
- The Introduction of Neural Networks (1950s): Frank Rosenblatt introduced the perceptron, which is the first single-layer neural network. However, it received a lot of backlash at the time and was limited by the technology of the era.
- Revival of Backpropagation (1986): Geoffrey Hinton and Yann LeCun developed backpropagation algorithms to train multi-layer neural networks from raw data more effectively.
- Modern Deep Learning Boom (2000s): Improved CPUs and GPUs allowed for more layers and deeper learning in models. They started being used for image recognition and search engine algorithms.
- Transformers and Large Language Models (2017 onwards): Researchers at Google introduced the Transformer architecture, drastically scaling deep learning and resulting in the AI systems that we use today.
Difference Between Deep Learning and Machine Learning
Deep learning is a subset of Machine learning, much like how algebra is just one of the topics in maths. Many people get confused between the two. So allow me to simplify the difference in deep learning and machine learning with the help of a table.
| Feature | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Data Requirements | Works with small-to-moderate datasets, benefits from more data | Performs best with large datasets |
| Feature Extraction | Learns with excessive programming by humans | Leans automatically by finding patterns in data |
| Model Type | Decision trees, SVMs, Linear Models, ensemble methods | Deep Neural Networks (CNNs, RNNs, Transformers) |
| Hardware | Mostly CPU | Uses GPUs and TPUs for the best performance |
| Training Time | Takes less time to train | Takes more time and computing power |
| Best Use Case | Structured/tabular data | Image, text, speech recognition |
Types of Deep Learning Models
Now that we know the basic differences between deep and machine learning models, let’s check out the different types of deep learning models used in AI and find out how they work.
1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
These deep learning models work best for images, videos, and similar datasets, which can be divided into a grid for easier processing. CNNs use a mathematical operation called convolution to learn about the different hierarchies of features in the image.
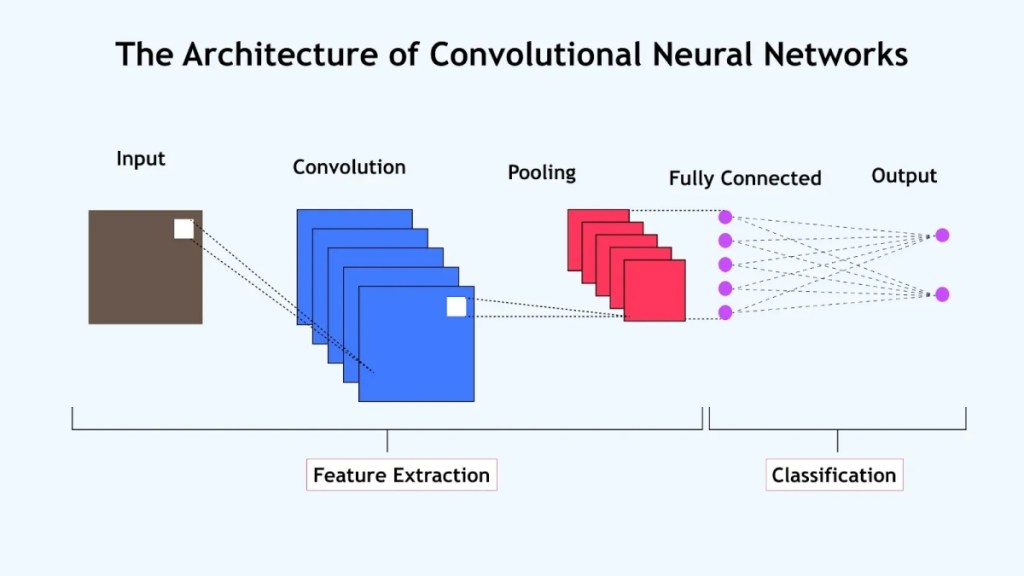
Like shapes, patterns, edges, and lines, and later move on to complex patterns (eyes, faces, wheels) in deeper layers. They are best for image recognition, Face ID on your iPhone, or object detection.
2. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
These are best for sequential data where the order of information matters, like text or speech. These RNN models process data in loops to allow previous information to influence the current step. Similar to how, when you read a sentence, you keep building a connection between every word.
3. Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTM)
The only issue with RNNs is that they tend to forget information, which is called the vanishing gradient problem. To overcome this issue, researchers use Long Short-Term Memory or LSTM networks, which use internal gates to regulate the flow of information. Common uses of LSTM deep learning are speech recognition and even generating AI music.
4. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
This deep learning model is used to generate AI images, music, and videos, and it’s a major part of Generative AI. It creates completely new, realistic data that was not in the training set. It consists of two components: a Generator that creates synthetic data and a Discriminator that tries to distinguish real from fake data. The two networks compete and improve each other’s performance.
5. Transformer Architecture (The Foundation of LLMs)
This is an improved approach for RNNs, being highly efficient at processing sequential data, especially text. It features a mechanism called Self-Attention, which allows the model to weigh the importance of different parts of the input data relative to each other.
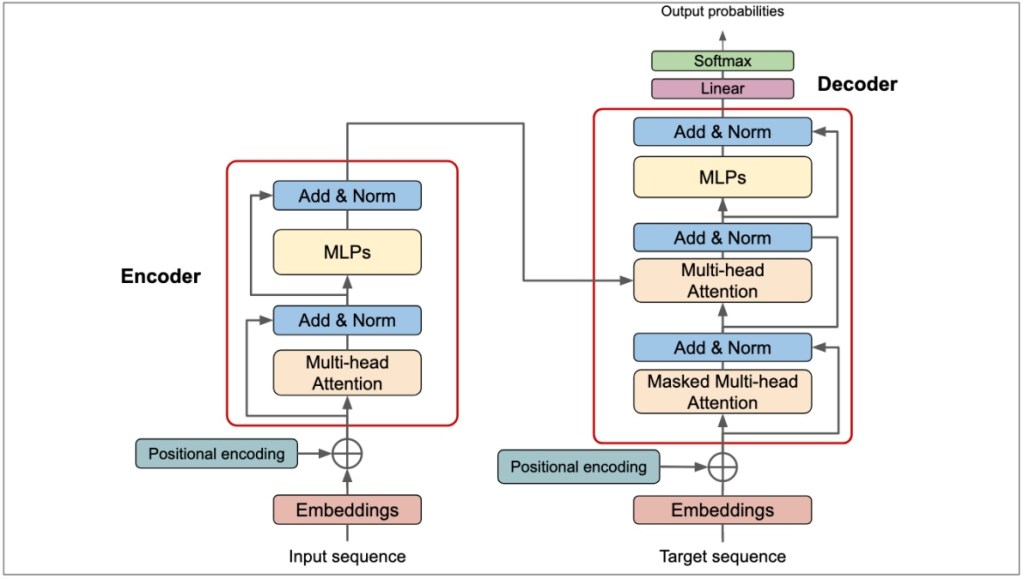
For example, when the input sentence contains “School”, the model will instantly focus on the context words like “Bus” or “Principal” to differentiate between the two meanings. The most common use of this deep learning architecture is seen in AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Copilot.
Applications of Deep Learning in AI
Deep learning in AI is widely used these days, and for a variety of situations and scenarios. Here are some major examples of the applications of deep learning.
- Image recognition
- Object detection
- Face and fingerprint scanning
- Chatbots and AI assistants
- Summarization tools
- Language translation
- Voice or music generation
- Image and video generation
- Personalized ads and recommendations
- Object tracking
- X-ray and MRI analysis
These are just some of the examples of areas in which deep learning in AI is being used. As the use of artificial intelligence grows further, so will the use of deep learning and its different models. It still surprises me that a concept from the 1950s is reshaping our current reality with innovations being made in every field, every single day.