- AI or Artificial Intelligence is a transformative technology that allows computer systems to mimic human-like intelligence.
- AI systems simulate many of the human qualities including learning, comprehension, decision making, problem solving, and more.
- Unlike traditional software which are explicitly programmed for each scenario, AI systems learn from statistical patterns in data.
With the launch of ChatGPT in late 2022, the world has not been the same. It kickstarted the AI revolution, turning what once felt like science fiction into reality. If you are still wondering what is AI and how it works, well, we have a solid explainer for you. You can learn about Artificial Intelligence, its history, how it works under the hood, and much more.
What is AI (Artificial Intelligence)?
Artificial Intelligence or AI is a groundbreaking technology that allows computer systems or machines to mimic human-like intelligence. It essentially enables machines to simulate many of the human qualities like learning, comprehension, decision making, problem solving, reasoning, etc. Just like humans, AI can understand language, analyze data, generate content, perceive the environment, and even perform actions.
AI is a field of research in computer science and when compared to established sciences like physics or mathematics, it’s a relatively young discipline, which was formally founded in 1956. However, AI has not been shaped by computer science alone, but researchers from linguistics, neuroscience, psychology, and even philosophy have contributed to this field.
All in all, AI is about developing a smart machine that is capable of thinking, learning, and performing actions like the human brain.
How Does AI Actually Work?
First of all, AI doesn’t work like traditional software which are pre-programmed to follow rigid, rule-based instructions. For instance, a calculator can only perform operations when given input in a certain syntax, and the output is fully deterministic.
However, AI systems can adapt to new inputs as they learn patterns from large datasets, so they can handle new inputs they were never directly programmed for. This makes AI systems probabilistic or non-deterministic.
Now, how does modern AI actually work? Well, it’s a technique called machine learning where systems learn patterns from data. AI systems are not explicitly programmed for every question or scenario, rather they are trained on massive amounts of data (text, images, videos, audio, code, etc.) which allows them to process new information and even generate meaningful response even for new inputs.
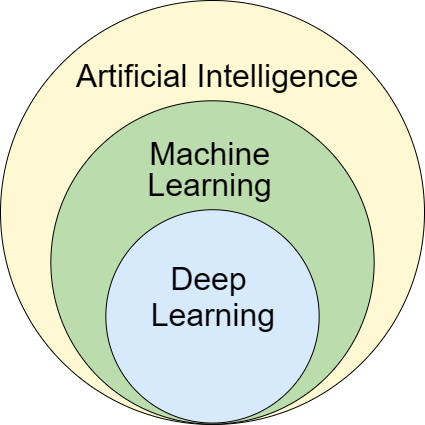
To give you an example, say you want to teach a child to recognize dogs. Now, instead of describing every dog feature, you show them multiple images of dogs. Eventually, they learn to identify dogs on their own, even those they have never seen before. And machine learning works exactly like that: it learns from examples (statistical patterns), and not explicit rules.
Now, in today’s time, the most powerful form of machine learning is deep learning which uses neural networks. Neural network is inspired by the human brain and it consists of layers of interconnected nodes like neurons to process information.
A Brief History of AI Development
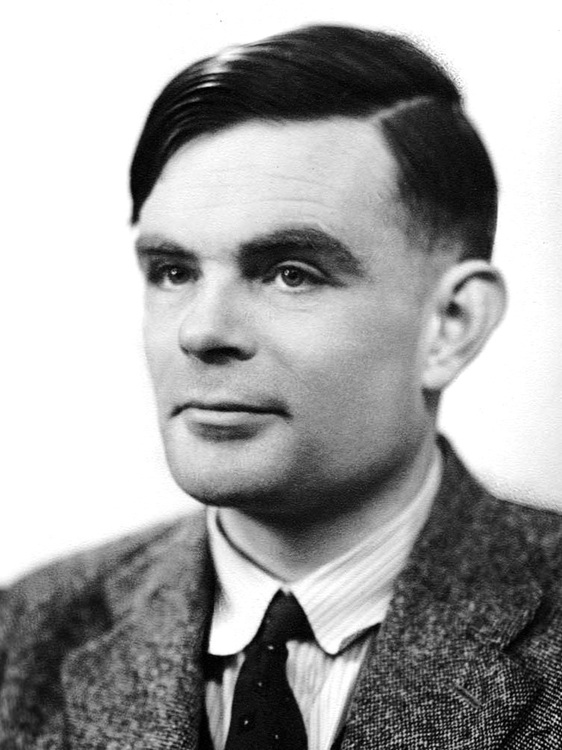
It may come as a surprise but the concept of AI appeared even before computers existed. In 1950, British mathematician Alan Turing posed a question: Can machines think? His famous Turing Test proposed that if a machine can carry a conversation indistinguishable from a human, it could be considered intelligent. This idea laid the foundation of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Now, the term “Artificial Intelligence” was officially coined in 1956 at a conference at Dartmouth College. AI researchers like John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon gathered to explore the idea of AI and whether machines could think like humans. This conference gave birth to AI as a formal field of study.

In the upcoming decades, there was an intense optimism around AI development, followed by disappointment. For many years, progress in AI stalled and funding dried up, leading to a period called “AI winters”. Early AI systems couldn’t understand natural language or recognize objects in photos, but they were effective at solving well-defined mathematical problems.
In the 1980s, some expert AI systems were trained for specific tasks, but they couldn’t adapt to new situations. Finally, in the 2010s, three things happened. Massive amounts of data came from the internet, powerful GPUs (originally designed for video games) became available, and a significantly better algorithm for deep learning came up.
In 2012, a neural network called AlexNet was released which outperformed all previous systems in recognizing objects in images. It started the AI renaissance period and then in 2017, Google researchers published a groundbreaking paper called “Attention Is All You Need” which introduced the Transformer architecture. Now, the Transformer architecture powers nearly all Large Language Models (LLMs) including GPT-5 and Gemini 3 Pro.
Types of AI
There are broadly two types of AI: narrow and general. Narrow AI is designed for a specific task like a song recommendation engine on Spotify, an object detection AI for images, or AI chatbots like ChatGPT. It’s excellent at what it’s designed for, but can’t perform tasks outside its domain.
On the other hand, general AI or Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) refers to AI systems with human-like ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across any domain. Essentially, AGI systems can match or surpass human capabilities. While AGI is still a fictional concept in the AI field, many labs including OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and Anthropic are working to achieve AGI.
Limitations and Challenges in AI
First of all, as AI systems are trained on massive datasets, if there are biases present in the data, AI systems also perpetuate those biases. For instance, if a dataset contains historical hiring data with gender discrimination, the AI system also learns to discriminate. AI companies are working to reduce biases in LLMs by cleaning the data before training them.
Apart from that, current AI systems don’t understand the world like humans do. While an AI system can beat world champions at chess or Go, it can’t match a child’s ability to understand the real world. Basically, AI models lack common sense and genuine understanding of the world.
Finally, the “black box” problem which is another challenge in the field of AI. AI researchers say that they don’t fully understand how AI thinks internally and comes to a particular conclusion. Understanding AI’s internal behavior is a key challenge in the AI field as we give more responsibilities and decision-making power to AI systems.