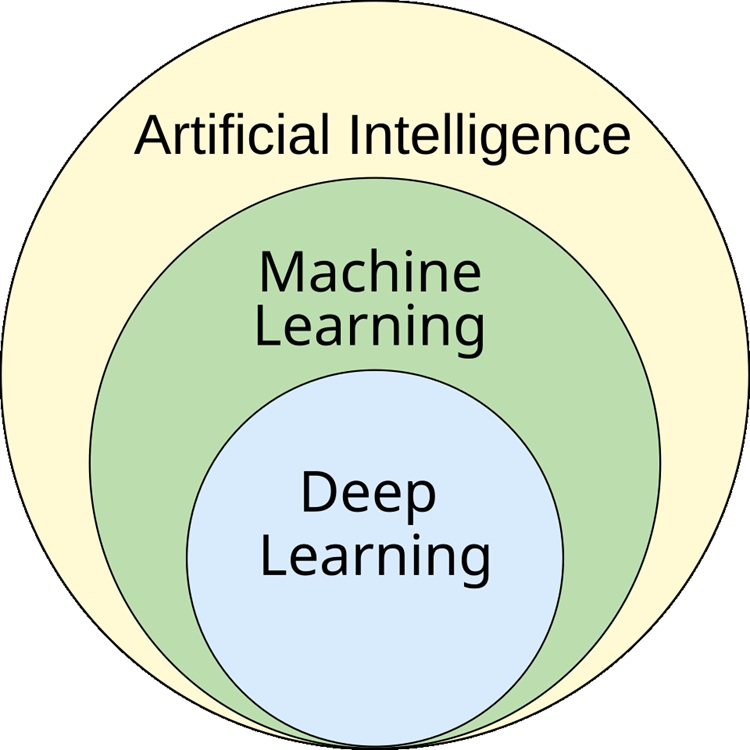
- Machine learning requires humans to manually label features while deep learning automatically learns features directly from raw data.
- ML uses traditional algorithms like decision tress, SVM, etc., whereas DL uses deep neural networks with multiple layers.
- Machine learning works well with small to medium datasets, but deep learning requires massive amounts of data.
In the field of artificial intelligence, both machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) play an important role in how the AI learns from raw data. However, they operate in different ways, yet still many people confuse them with each other. So let me help clear your doubts and explain the difference between deep learning and machine learning in this read.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning models or algorithms can learn from data and make predictions on their own. They don’t need humans to explicitly program every rule for how to learn and come up with an output. Hence, the ‘learning’ part. However, in traditional machine learning, humans do need to manually label every single data feature.
For example, if you want it to know what a cat looks like, you need to state its distinct features, like ears, whiskers, tail, and paws. This is why traditional Machine learning is best suited for small-scale structured data sets.
Types of Machine Learning Models
The field of machine learning is quite vast and encompasses deep learning as a subset, but there are primarily three main types.
- Supervised Learning: This machine learning model uses labeled data where the features and target are clearly outlined. This helps to minimize prediction errors and is typically used in identifying spam emails or predicting house prices.
- Unsupervised Learning: Unsupervised learning algorithms are given unlabeled data, like an image, and they learn patterns and relations independently. They do so by making clusters and using multiple hidden layers of neural networks.
- Reinforcement Learning: This model learns from its environment based on a trial-and-error method. It will make random predictions till it gets one right, and it will be rewarded for it. On the other hand, it can also be penalized for making a wrong guess. This algorithm is commonly seen on robots and self-driving cars.
Use Cases of Machine Learning Models
Machine learning in Artificial Intelligence has become quite common lately, and the demand has increased in a lot of fields. Here are some everyday applications of these models:
- Spam mail detection and email classification
- Recommendation engine and personalised ads
- Fraud detection and flagging suspicious activities
- Search engine ranking, like the one used by Google
- House price prediction
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning, as I have explained above. Unlike traditional machine learning, deep learning can automatically learn features from raw data without manual feature engineering. The data can be labeled or unlabeled, depending on the task.
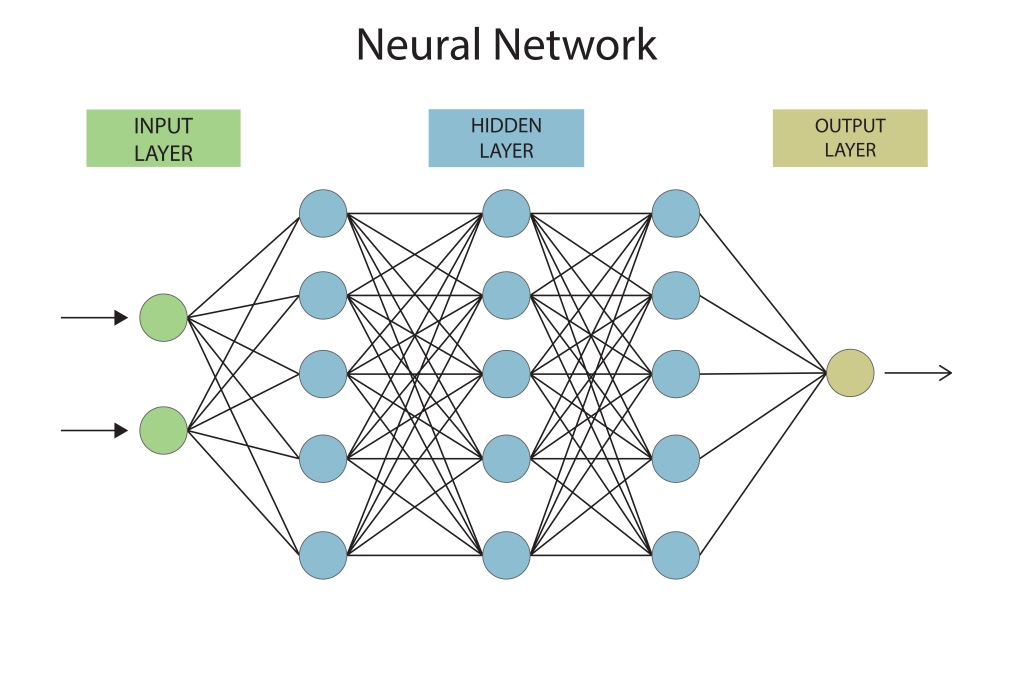
It does so by using multiple hidden layers of neural networks that automatically extract and learn increasingly complex patterns. Deep learning is being widely used today in AI chatbots, image generators, video and music creation, large language models, as well as language translations.
Types of Deep Learning Models
Similar to machine learning, deep learning models also have a variety of architectures based on different use cases. Here’s a breakdown of them.
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Use convolutional filters to automatically extract features from visual data, detecting patterns like edges, textures, and objects. Best suited for images and videos.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Process sequential data by maintaining information from previous steps. It allows the network to understand context and order. Mostly used in speech recognition and digital assistants.
- Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTM): It is a type of RNN that addresses the vanishing gradient problem, allowing the network to retain information over longer sequences. They are used for complex things like language models.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN): This is made up of a Generator and a Discriminator neural network, where one creates new data to try to fool the other one. It is used to make AI images, videos, text, and music.
- Transformer Architecture: This is the pillar of today’s large language models like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and Microsoft Copilot. It features a component called Self-Attention which prioritizes certain parts of data over others.
Use Cases of Deep Learning Models
Deep learning is a branch of machine learning, but its use has evolved a lot, and it is being widely adopted in various industries. Here are a few examples.
- Image and object recognition
- Large language models like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Copilot
- Image, video, and music generation
- Building personalized social media algorithms for apps like TikTok, YouTube, and Instagram
- Converting spoken language into text
Deep Learning vs Machine Learning: Key Differences
Now that we have taken a good look at both models, it is time we finally compare the two and find out the differences between machine learning and deep learning.
| Feature | Machine Learning (ML) | Deep Learning (DL) |
| Data Size | Works well with small to medium datasets. | Requires massive amounts of data to reach peak performance. |
| Hardware | Can run on standard CPUs. | Requires high-end GPUs or TPUs for training. |
| Feature Extraction | Requires human feature engineering. | Features are learned directly by the network. |
| Architecture | Uses traditional algorithms (decision trees, SVM, etc.) or shallow neural networks | Uses Deep Neural Networks (3+ hidden layers). |
| Performance | Performance often plateaus as data volume increases. | Performance continues to increase with increasing data volume. |
| Interpretability | Easier to understand how the model arrived at its decision (less of a “black box”). | Harder to interpret the decision-making process (“black box”). |